Feb 17, 2026
Mar 02, 2026

Understand working capital, its components, why it matters, and how working capital loans can help businesses maintain cash flow
- Quick Summary
- What: A complete guide to working capital, meaning, components, types, and how it impacts business operations.
- Why: Helps business owners understand the role of working capital in managing daily expenses and operational liquidity.
- Who: Entrepreneurs, SMEs, MSMEs, and finance teams looking to improve financial management and access funding.
- How: By exploring working capital definition, management techniques, loan options, and practical insights to strengthen cash flow.
- Use Case: Useful for businesses planning inventory purchases, payroll funding, vendor payments, or seasonal scaling, and considering working capital loans.
Working capital is the cornerstone of business finance, representing the funds a company needs to keep its day-to-day operations running smoothly. It measures a business’s short-term financial health and operational liquidity, enabling firms to meet immediate expenses such as inventory purchases, payroll, supplier payments, and unexpected costs.
Proper working capital management helps businesses maintain cash flow, avoid unnecessary borrowing, and stay prepared for growth opportunities, especially important for SMEs and MSMEs, where operational liquidity can make or break ongoing performance. In this guide, we explain what working capital is, its components and types, the working capital lifecycle, common loan options, and how to manage it to support business stability and growth.
What is Working Capital?
Working capital is the difference between current assets and current liabilities, indicating the cash available for a business to run its day-to-day operations and cover short-term obligations.
This metric reflects your business’s liquidity and short-term financial strength. Positive working capital means your current assets exceed current liabilities, giving you sufficient funds for expenses like rent, payroll, inventory purchases, and emergency costs. Negative working capital indicates potential liquidity issues, as obligations may exceed readily available resources.
Importance of Working Capital Management
Managing working capital effectively ensures your business can meet short-term financial obligations without disruption. It maintains liquidity, enables timely payments to suppliers and employees, minimises costs related to delayed payments, and supports stable operations even during slow seasons.
Efficient working capital management also enhances your creditworthiness and makes it easier to secure financing when needed.
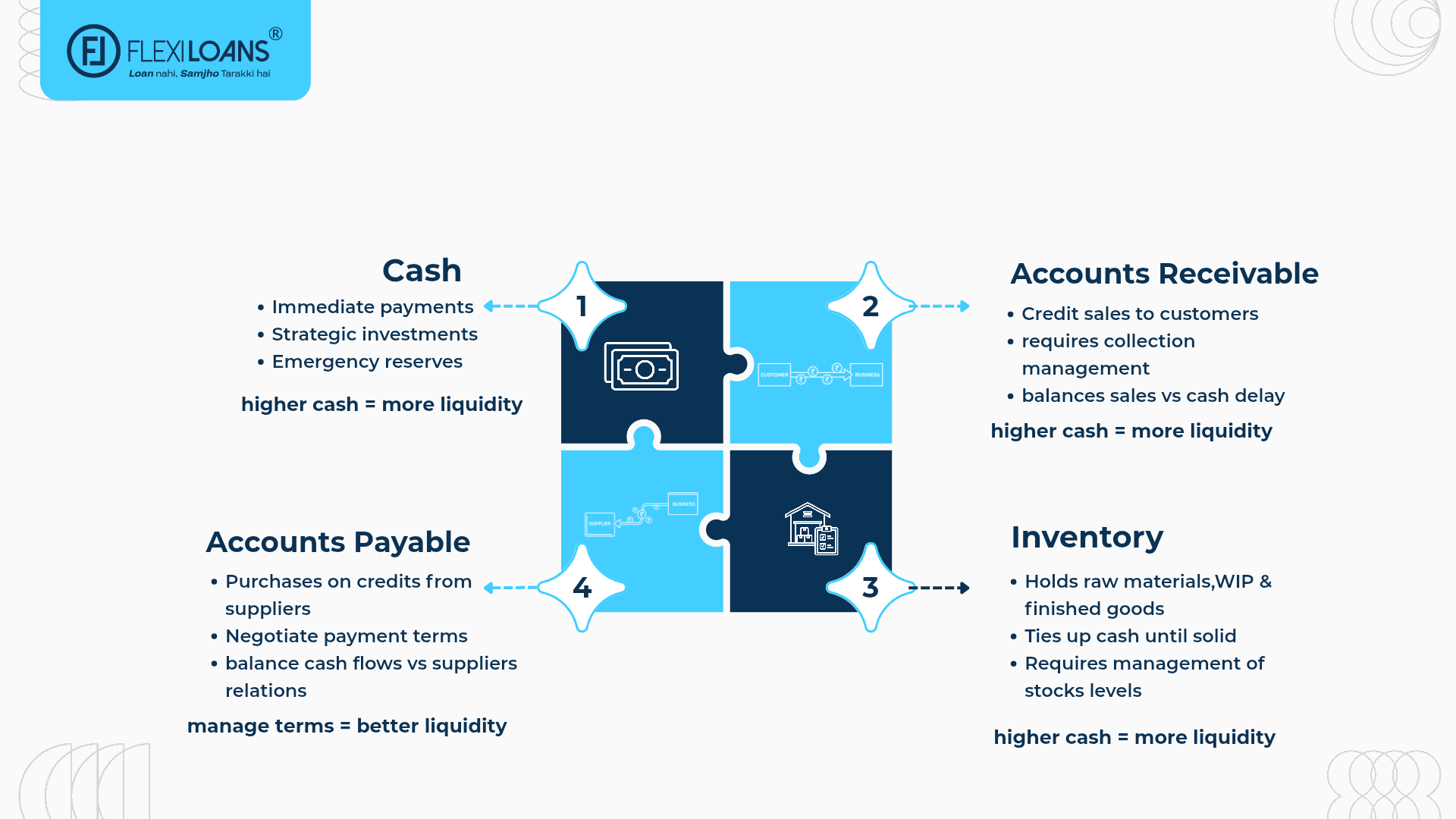
Components of Working Capital
Working capital is made up of several key elements:
- Cash: The most liquid form of working capital used for immediate expenses like payroll and utilities.
- Accounts Receivable: Money owed by customers that can be collected to improve cash flow.
- Inventory: Goods held for sale or for use in production; optimal levels help avoid overstocking.
- Accounts Payable: Short-term obligations owed to suppliers; managing payment timing can preserve cash.
Types of Working Capital
There are several forms of working capital used in business finance:
1. Permanent Working Capital:
This is the base level of working capital required year-round, regardless of seasonality or business cycles. It ensures that core operational costs, such as salaries and rent, are always covered.
2. Temporary or Variable Working Capital:
This fluctuates with demand, production volume, and seasonal trends. Businesses may need more working capital during peak periods like festivals, harvests, or year-end sales.
Working Capital Loan Options
This section lists common financing options that help support working capital needs:
- Term Loan – Lump sum financing repaid over time, suitable for predictable working capital needs.
- Line of Credit – Flexible funding up to a limit, interest charged only on the amount used.
- Invoice Financing – Advance against unpaid invoices to improve cash inflow.
- Trade Credit – Buy now, pay later arrangements with suppliers.
- Working Capital Loan – Dedicated loan specifically for daily operational costs.
- Machinery Loan – Helps fund equipment purchases that indirectly support operational efficiency.
Factors Affecting Working Capital
- Business Size: Larger businesses require higher working capital due to increased inventories, larger operational costs, and the need for greater financial flexibility to manage extensive operations.
- Business Cycle: Seasonal businesses, like retail, face varying needs. During peak seasons, they require higher working capital to handle increased demand, while off-peak cycles allow them to scale back.
- Production Cycle: Industries with longer production cycles, such as manufacturing, need more working capital as funds remain tied up in production and raw materials for extended periods, slowing down cash conversion.
- Credit Terms: The credit terms set with suppliers and customers directly affect cash flow. Longer credit terms result in delayed cash inflows, which can impact liquidity and increase the demand for working capital to maintain smooth operations.
Factors influencing capital requirements vary across business size, industry, seasonality, and credit terms. Larger enterprises typically need more funds to support extensive inventories and operational costs. Seasonal businesses, like retail, experience fluctuating capital needs, with higher demands during peak periods. Manufacturing companies, especially those with longer production cycles, face challenges in managing capital due to funds remaining tied up in materials and production processes. Additionally, credit terms with suppliers and customers impact cash flow, as longer terms delay inflows, affecting liquidity.
Sources of Working Capital
Here’s a look at common options:
- Internal Sources: Profits, retained earnings, or asset sales.
- External Sources: Business loans, trade credit, or short-term borrowing.
- Long-Term Sources of Working Capital: Equity financing and long-term loans support stable cash flow, especially for permanent working capital needs.
For hassle-free financing, platforms like FlexiLoans offer various loan options. With FlexiLoans, the process of applying for a business loan becomes simpler, and they offer collateral-free loans designed for diverse needs.
Features of Working Capital
Working capital has unique features that make it a cornerstone of business finance:
- Short-Term Nature – Supports immediate operational requirements.
- High Liquidity – Quickly converts into cash for expenses.
- Variable Demand – Fluctuates based on business needs and production cycles.
- Limited Return – It doesn’t generate profit directly but supports operational sustainability.
Permanent vs. Temporary Working Capital
- Permanent Working Capital: Always required for essential operations.
- Temporary Working Capital: Needed for specific, short-term demands, such as increased production during peak times.
By balancing permanent and temporary working capital, businesses ensure smooth operations while remaining financially flexible.
How to Apply for a Working Capital Loan
Getting this loan has become simpler, especially with platforms like FlexiLoans that streamline applications. Here’s a breakdown of what you need:
- Eligibility for Business Loan: Confirm your business qualifies by reviewing eligibility criteria.
- Documents Required for Business Loan: Collect essential documents like tax returns, financial statements, and business proof.
- EMI Calculator for Business Loan: Use the business loan EMI calculator to plan monthly instalments.
Benefits of Working Capital Loan
They offers several advantages, helping businesses like yours manage cash flow effectively:
- Quick access to funds to cover operational expenses
- Often unsecured, making them accessible for small businesses
- Flexible repayment terms that align with cash flow
- Ability to cover operational costs, allowing reinvestment in growth
- Improved liquidity to meet financial commitments without stress
By leveraging the right working capital financing options, businesses can maintain a healthy financial foundation, navigate challenges, and seize opportunities for growth.
Working Capital Life Cycle
The working capital life cycle refers to the time required for a business to convert its total net working capital to cash. Additionally, it reflects an organization’s skill and willingness to handle its short-term liquidity. In other words, it is the period between the acquisition of raw materials and the generation of money through the sale of produced items.
A business can attempt to reduce the length of its working capital cycle in the following ways:
- Reduced credit duration granted to clients, resulting in a shorter average collection duration. Additionally, providing a cash discount might help enhance the debtor’s turnover percentage or average collection time frame, among other things.
- The business might take initiatives to enhance or streamline its production processes and concentrate on alternative sales methods. This will result in a reduction in the time required to convert inventory to sales. The faster earlier stock is cleared, the more favorable the working capital cycle will be.
- Additionally, the working capital cycle can be decreased by improved negotiation with suppliers of raw materials and items necessary for manufacturing to extend the credit duration.
The formula is:
Working capital life cycle = Sum of inventory days + Receivable days – Payable days
A good strategy to abbreviate this life cycle is to improve the business venture’s competency and liquidity in the short term. Generally, this is accomplished by selling merchandise, creating revenue through sales, and progressively repaying current debts.
Effective working capital management is the backbone of business sustainability. Businesses that monitor liquidity, optimize inventory, and leverage the right financing options can not only avoid cash crunches but also capitalize on growth opportunities.
Conclusion
Working capital is essential for every business, serving as the financial foundation for daily operations and short-term obligations. By understanding its components, managing it effectively, and choosing the right financing option when needed, businesses can maintain liquidity, sustain smooth operations, and unlock opportunities for growth. Whether you require a line of credit, invoice financing, or a dedicated working capital loan, choosing the right solution can help your business thrive even during high demand or slow seasons.
FAQs: Working Capital
Ans: It ensures that a business can meet its short-term financial obligations, such as payroll, supplier payments, and inventory purchases.
Ans: Cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and accounts payable are the core components.
Ans: Term loans, lines of credit, invoice financing, trade credit, and specific working capital loans all support operational liquidity needs.
Ans: You can apply through platforms like FlexiLoans, offering online applications with minimal documentation.
Ans: Factors like business size, production cycle, seasonality, and credit terms impact working capital needs.
Ans: Working capital is the difference between a business’s current assets and current liabilities, reflecting its ability to cover day-to-day expenses.
Ans: Working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities. A positive number indicates sound liquidity.
Ans: Yes. Negative working capital means current liabilities exceed current assets, indicating potential liquidity issues.
Ans: Improve collections, manage inventory efficiently, negotiate better credit terms with suppliers, and use short-term financing wisely.
Glossary: Key Terms Explained
| Term | Definition |
| Working Capital | The difference between a company’s current assets and current liabilities indicates short-term financial health. |
| Current Assets | Assets expected to be converted into cash within one year, such as cash, receivables, and inventory. |
| Current Liabilities | Short-term financial obligations due within one year, such as payables and short-term debt. |
| Liquidity | A business’s ability to cover its short-term obligations. |
| Line of Credit | A flexible loan where funds can be drawn as needed up to a limit. |
| Invoice Financing | A type of financing where unpaid invoices are used as collateral for an advance. |
| Trade Credit | Supplier credit allows deferred payment, helping preserve cash flow. |
| Working Capital Loan | A loan dedicated to financing day-to-day business operations. |
| Operating Cycle | The time required to convert working capital into cash through normal business activities. |
| Cash Flow | Movement of cash in and out of a business over time. |
Is this information helpful?




